XFS is a high-performance 64-bit journaling file system created by Silicon Graphics, Inc in 1993. The file system was ported to the Linux kernel in 2001. Currently, XFS is supported by most Linux distributions, some of which use it as the default file system. XFS is a 64-bit file system and supports a maximum file system size of 8 exbibytes minus one byte. (263 − 1 bytes)
1 exbibyte = 260 bytes
Features :
- Capacity
- Journaling
- Allocation groups
- Striped allocation
- Extent based allocation
- Variable block sizes
- Delayed allocation
- Sparse files
- Extended attributes
- Direct I/O
- Guaranteed-rate I/O
- DMAPI
- Snapshots
- Online defragmentation
- Online resizing
- Native backup/restore utilities
- Atomic disk quotas
Creating XFS File System :
- You need to create a partition using fdisk or some other command as below. In below example, we are creating 1 GB partition.

2. Now update the changes in partition table to kernel.
# partprobe /dev/xvdb
3. Check using fdisk command as below
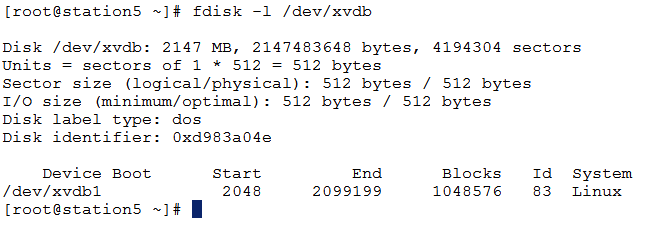
4. Install xfs tools as below
# yum install xfsprogs -y
5. Format the newly created drive using mkfs.xfs command as below.
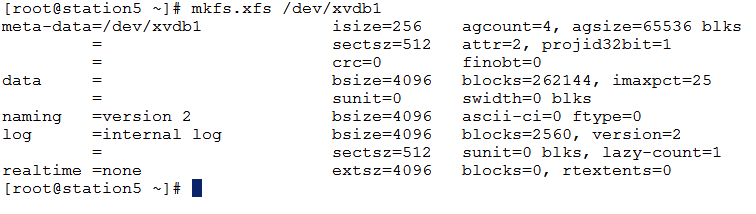
6. Mount the newly created drive to some folder say /mnt
# mount /dev/xvdb1 /mnt
7. You should be able to check the status using df -h command.
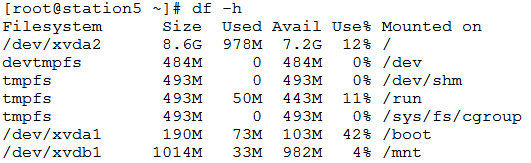
8. That’s All ! You did it . . .